Sunburn is a common issue that can affect people of all ages and skin types when time is spent in the sun. It goes beyond just discomfort and can be a serious problem.
In this article, we will explore the different types of sunburns and how it impacts various skin tones.
We will also discuss the potential risks associated with sunburn, including long-term consequences such as skin cancer and premature aging.
Most importantly, we will provide straightforward steps to help you and your children stay safe in the sun.
So, grab your sunscreen, and let’s learn how to protect ourselves from the sun’s harmful effects.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Sunburn?
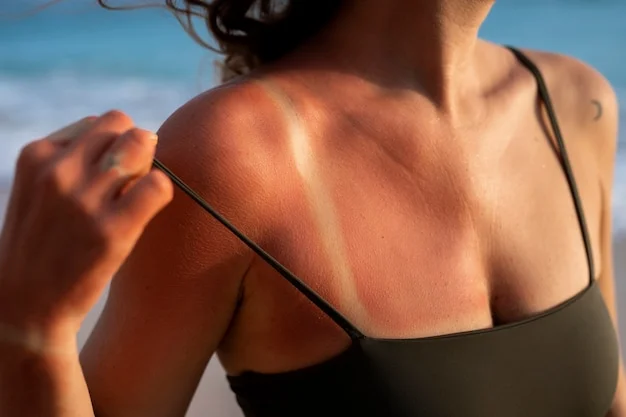
A sunburn is skin damage that occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation (harmful invisible light from the sun).
Such exposure can damage the DNA of skin cells which could cause various health problems such as premature aging, and skin cancers, including melanoma.
According to the Canadian skin cancer foundation, about 90% of skin cancers are caused by UV rays.
Types of Sunburn and Their Effects on Lighter, and Darker Skin Tones
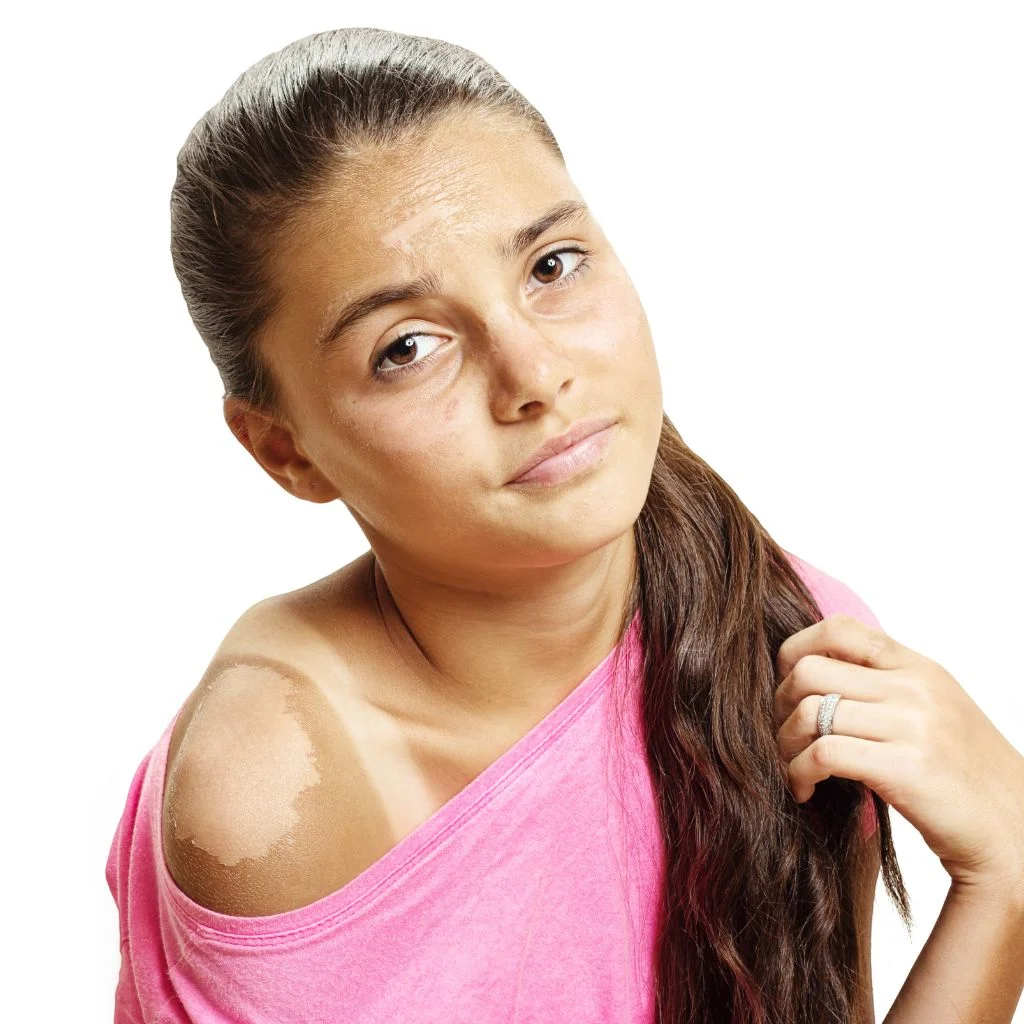
Sunburn can present differently depending on skin tone, with lighter-skinned individuals often experiencing redness, heat, pain, and tightness, while those with darker skin may not see visible redness but may feel heat, sensitivity, and itchiness.

Peeling can occur in both cases.
When your skin absorbs UV rays, some people get a tan. This happens because certain skin cells called melanocytes produce a brown pigment called melanin.
A tan is your body’s attempt at protecting itself from further damage.
Melanin helps protect against UV rays, so dark-skinned people are less likely to burn in the sun, unlike fair-skinned people who are more prone to burns.
How Long Does Sunburn Last?
Typically, sunburn will improve within a week – sunburns typically appear 2-6 hours after sun exposure, peak in intensity within 24 hours, and usually fade within 48 hours.
Keep in mind that the time it takes for a sunburn to heal depends on how severe it is.
When it’s mild, you’ll typically experience redness, some pain, and a bit of skin peeling for about three to five days.
For moderate sunburns, expect roughly a week of healing time, marked by redness, swelling, and hot skin.
Severe sunburns, on the other hand, might need a doctor’s attention, given their painful blisters and intense redness. Recovery can extend up to two weeks, and it’s essential to take it easy at home for proper healing.
If you experience sunburn along with any of these symptoms, it’s recommended to consult your doctor or healthcare provider:
- Shivering
- High fever
- Muscle cramps
- Headaches
- Skin blistering or swelling
- Persistent feelings of fatigue, dizziness, or nausea
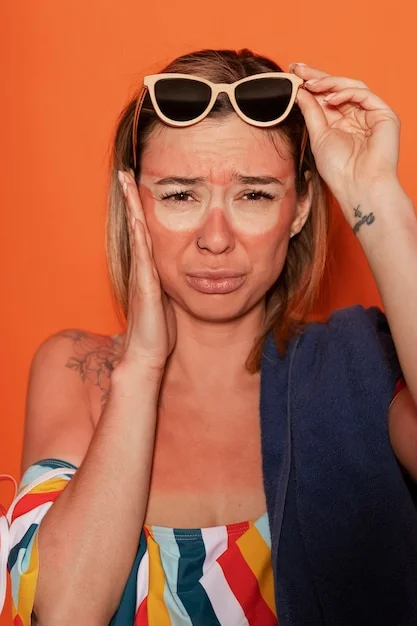

Keep in mind that UV light damage risk is increased by various factors regardless of skin tone, such as:
- Personal and family history of skin cancer,
- Tendency to burn easily,
- Living in high altitudes or tropical regions,
- Outdoor activities,
- Weekend sun exposure after indoor work weeks,
- Autoimmune disorders
- Medications that lower or suppress your immune system
- Medications that make your skin more sensitive to sunlight (photosensitizing medication)
Individuals with these risk factors should take extra precautions in the sun.
Long-Term Risks and Complications of Sunburn
Sunburn can cause skin cancer
Sunburn can increase your risk of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are more common but less lethal, while melanoma is responsible for most skin cancer fatalities.
Early detection is crucial, as non-melanoma skin cancers can progress to malignant melanoma.
In a 2016 study, it was discovered that melanoma risk is highest among whites, then American Indians, Hispanics, Asians, Pacific Islanders, and finally, blacks.
Surprisingly, darker skin tones face more severe outcomes from skin cancer.
The study revealed higher skin cancer death rates among individuals with darker skin is often due to late-stage diagnosis.
Premature aging
Excessive sun exposure can harm your skin, causing premature aging characterized by wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.

When skin gets sunburned, the aging process, known as photoaging, speeds up. UV light weakens skin’s connective tissues, leading to reduced firmness and flexibility.
This results in deep wrinkles, dryness, red veins on the face, freckles mainly on facial areas, and dark spots on exposed skin like the face, hands, arms, chest, and upper back.
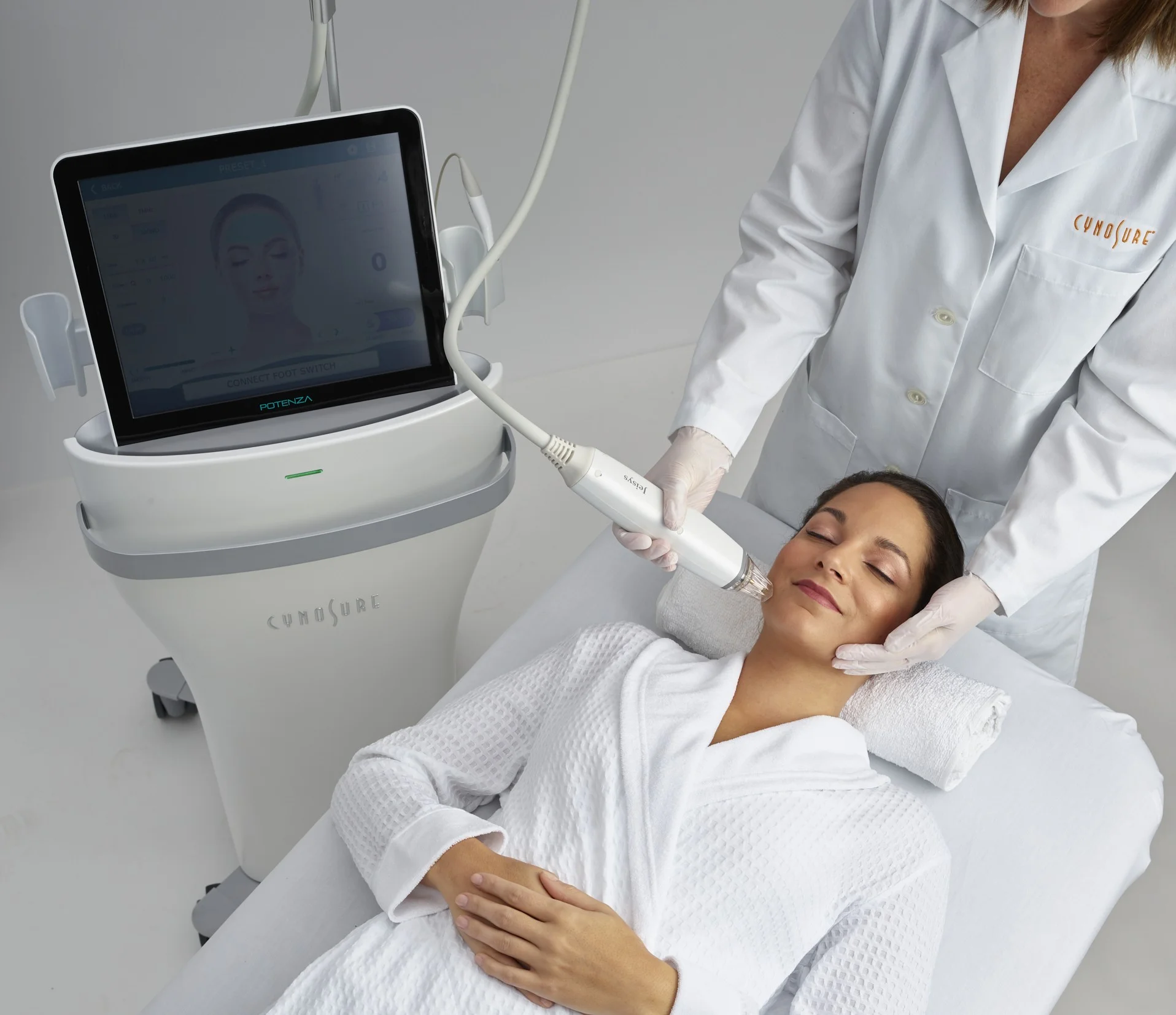
Some advanced treatments you should consider in addressing these skin concerns include:
Laser therapy and Potenza RF microneedling have been shown to be successful in removing wrinkles, fine lines and age spots.
These treatments promote the production of collagen and elastin, which improves the quality of your skin.
Additionally, they are minimally invasive, require little downtime, and are suitable for a variety of skin types and conditions.
Eye problems
Over time, sun exposure can damage your eyes and increase your risk of developing macular degeneration and cataracts – when the lens in the eye becomes cloudy.
People who suffer from sunburned eyes (photokeratitis) may experience discomfort or a gritty sensation.
Also known as snow blindness (when UV rays are reflected off snow and ice), this eye condition is temporary and your symptoms can last a few hours to a few days.
In addition to sun exposure, other sources of UV light, such as welding, tanning lamps and faulty mercury vapor lamps can also cause this condition.
Weakened immune system
Prolonged exposure to sunlight can weaken your immune system, which plays an important role in protecting your body against the harmful effects of sunlight (UV radiation in particular).
A weakened immune system, combined with sun damage, can hinder the body’s ability to fight skin conditions and reduce the effectiveness of medications used to treat such damages.
Sunburn Prevention and Treatment
How To Treat Sunburns
Unfortunately, there is no immediate solution to treating a sunburn. Once a sunburn has happened, the damage has been done.
However, as time passes, your body will naturally begin the healing process by shedding the outer layer of damaged skin.
Don’t try to peel the skin yourself. Let it come off naturally.
In the meantime, to effectively address sunburn and ease discomfort, it’s important to take prompt action upon noticing the signs.
The first step involves moving away from direct sunlight and finding shelter, preferably indoors.
Once indoors, following these recommendations will help treat the sunburn and relieve your discomfort:
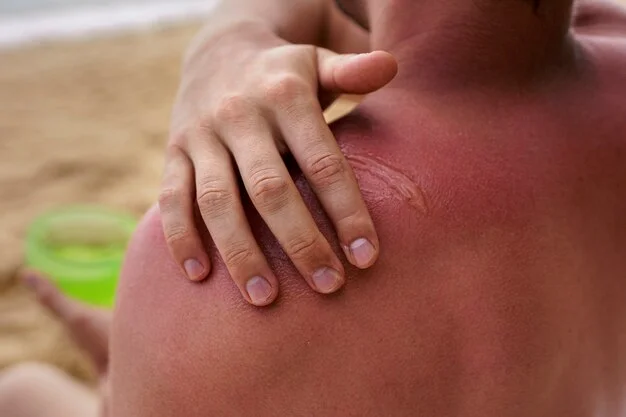

- Take brief, refreshing baths or showers to ease discomfort. Use mild soap to prevent further irritation. Afterward, gently pat your skin dry, leaving some moisture. You can also use cold compresses for relief, but avoid applying ice directly to the sunburn.
- Afterwards, apply a moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated and prevent dryness. Choose a moisturizer with aloe vera or soy to soothe sunburned skin (avoid petroleum or oil-based products, as they can worsen the burn). If certain areas are particularly uncomfortable, you can apply over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream as instructed on the label to reduce redness and swelling.
- Avoid sunburn treatment products or medicated creams containing “caine” ingredients like benzocaine, as they may irritate or trigger allergies.
- Wear loose, soft clothes to prevent more irritation, and stay out of the sun until your skin heals.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Sunburns draw fluid to the skin’s surface and away from the rest of the body, which can lead to dehydration. Drinking extra water helps prevent this.
- If blisters appear, this means you have sustained a second-degree burn. Blisters must be allowed to heal naturally. Popping them could slow healing and raise infection risk. Watch for signs like red streaks or pus.
- Make sure to shield your sunburned skin as it heals. Opt for clothing that covers well, especially fabrics with a tight weave. Here’s a handy tip: if no light passes through the fabric when held against a bright light, it offers enough protection.
- If you are unable to shield the area with clothing, then a 100% mineral sunscreen like EltaMD’s UV Physical which contains 9.0% Zinc oxide, 7.0% Titanium dioxide, and antioxidants to reduce free radicals and help diminish the visible signs of aging is your best alternative.

For Children:
Your baby’s skin is delicate, pure, and sensitive. It’s quick to develop irritation but responds well to gentle creams.
Baby skin heals faster, but it’s not great at shielding against the sun. Babies under 6 months must avoid sun exposure, and older babies need protection, like UV-blocking sunglasses.
If your child gets sunburned, follow these steps:
- Bathe the skin in clear, tepid water to provide a cooling effect.
- In the case of a baby under 1 year old, it is crucial to treat sunburn as an emergency and immediately contact your doctor.
- For a child who is 1 year or older, it is advised to call your doctor if there are symptoms such as severe pain, blistering, lethargy, or a fever.
- Sunburn can lead to dehydration, so it is important to offer your child water or juice to replenish body fluids.
- If the child is not urinating regularly, this should be considered an emergency and medical attention should be sought.
- To soothe the skin, apply a light moisturizing lotion without rubbing it in. If necessary, dab plain calamine lotion, but avoid using any with added antihistamine.
- It is important not to apply alcohol, as it can excessively cool the skin.
- Medicated creams such as hydrocortisone or benzocaine should not be used unless specifically instructed by your pediatrician.
- Until the sunburn has healed, keep your child completely out of the sun. It is essential to practice sun protection and ensure that sun safety is prioritized wherever your child goes.
How to Prevent Sunburn
Even after your skin heals from a sunburn, the damage has been done. It’s necessary to protect yourself from the sun, not just during outdoor activities, but every day.
Fortunately, there are simple ways to prevent sunburn, no matter your skin type or what you’re doing. Here are a few tips:
- Wear sunscreen. To shield your skin from sunburn, use a broad spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or more. Cover all exposed areas: face, neck, ears, lips, and hands. Reapply every two hours, or sooner if sweating or swimming, to keep the protection strong.

- Wear protective clothing. Protective clothing, such as hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves and pants, can help to protect your skin from the sun.
- Limit your time in the sun and seek shade. Avoid spending too much time in the sun and seek shade whenever possible, especially during the middle of the day when the sun’s rays are strongest (between 10 am and 4 pm).
Choosing the right sunscreen for Sunburn
When choosing a sunscreen, it is important to consider the following factors:
SPF. SPF stands for sun protection factor. It measures how well a sunscreen protects against UVB rays, which are the rays that cause sunburn. Look for a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Broad-spectrum protection. Broad-spectrum protection means that the sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVB rays play a greater role in causing skin cancers, including malignant melanoma.
Apart from causing skin cancer, UVA rays also lead to premature skin aging, including the formation of wrinkles, as they can penetrate deeper into the skin.
It is important to note that sunlight contains around 500 times more UVA rays than UVB rays. Therefore, protecting the skin from UVA rays is just as important as shielding it from UVB rays.
Choosing a sunscreen that provides broad-spectrum protection, like EltaMD® Skincare, is essential.
Conclusion
To sum up, sunburns are a serious issue, causing discomfort and long-term health problems like skin cancer and premature aging.
Recognizing its effects on different skin tones and understanding when to seek medical help is crucial. Prevention through sunscreen, protective clothes, and limited sun exposure is vital.
Staying hydrated, using gentle skincare, and seeing a doctor when necessary are important for managing sunburn. Prioritizing sun safety is essential for immediate relief and long-term well-being.
Additional Resources:
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/sun-and-uv/sun-damage
https://uihc.org/health-topics/what-difference-between-uva-and-uvb-rays
https://www.pureluxemedical.com/blog/the-damaging-effects-of-the-sun

Dr. Lian Peter, MD, MPH, CCFP, is a Family physician with a passion for aesthetics. In her aesthetic clinic, she provides a wide range of minimally invasive and non-invasive procedures, constantly honing her skills to deliver exceptional care and help patients attain their desired appearance.